목적
- deepops를 이용해서 필요한 환경을 구성할 수 있다.
- deepops를 이용해서 GPU 모니터링을 위한 prometheus, grafana 환경을 구성할 수 있다.
실천 목표
- deepops를 이용해서 nvidia driver, docker, prometheus, grafana를 설치하고 모니터링한다.
- deepops를 이용해서 (nvidia driver, docker 설치는 되어 있다고 가정하고 ★) prometheus, grafana를 설치하고 모니터링한다.
deepops 개요
- https://github.com/NVIDIA/deepops
- GPU 인프라 및 자동화 도구
deepops를 이용한 테스트 환경 구성
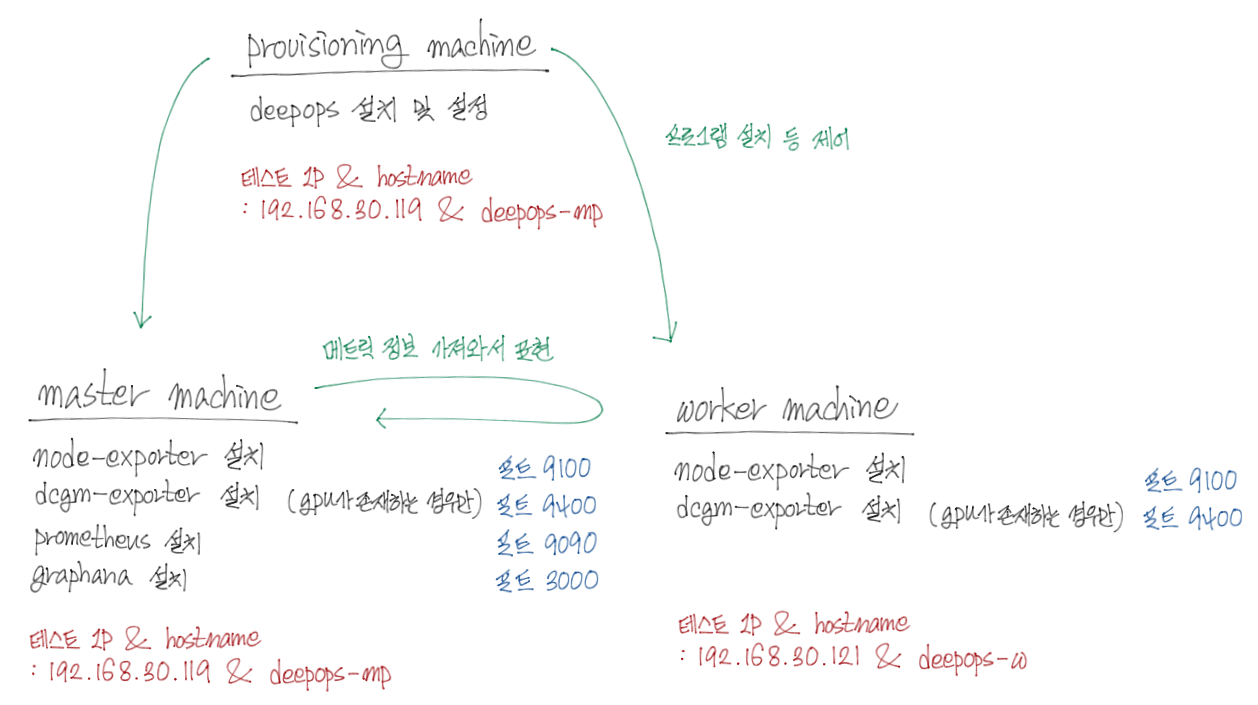
- 테스트 구성도
![deepops_test]() Copyrightⓒ2022 Develiberta All rights reserved.
Copyrightⓒ2022 Develiberta All rights reserved.- 테스트는 deepops 22.04.2 버전을 기준으로 작성되었으며, OS는 Ubuntu 20.04 LTS를 설치했다.
- master 노드에 gpu가 있는 경우, provisioning 노드와 master 노드를 하나의 서버로 통합하지 않는다. (위의 그림처럼 하는 경우 별도의 작업 필요) 왜냐하면 provisioning 노드에서 각 노드(master 노드와 worker 노드)에 필요한 프로그램을 설치하는 과정에서 각 노드가 재부팅될 가능성이 있는데, 설치를 주관하는 provisioning 노드가 재부팅되면 설치가 비정상적으로 종료되기 때문이다.
- 파일 내에서 추가나 변경 또는 삭제가 필요한 부분은 ☆로 표시했다.
- 모든 노드에 지원되는 OS를 설치한다. 지원되는 OS는 다음과 같다.
- NVIDIA DGX OS 4, 5
- Ubuntu 18.04 LTS, 20.04 LTS
- CentOS 7, 8
- provisioning 노드에서 기본적인 deepops를 설치한다.
1 2 3
$ git clone https://github.com/NVIDIA/deepops.git $ cd deepops $ ./scripts/setup.sh
- provisioning 노드에서 deepops inventory를 수정한다.
1
$ vi ./config/inventory
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18
[all] # ☆ 다음을 추가 (이때, 각 서버의 hostname과 IP를 동일하게 추가) deepops-mp ansible_host=192.168.30.119 deepops-w ansible_host=192.168.30.121 [slurm-master] # ☆ 다음을 추가 deepops-mp # master 노드 [slurm-node] # ☆ 다음을 추가 deepops-mp # master 노드에 대해서도 모니터링하고자 하는 경우에만 추가 deepops-w # worker 노드 [all:vars] # SSH User # ☆ 다음을 추가 ansible_user=nvidia # ansible을 이용할 사용자명
- provisioning 노드에서 deepops inventory가 정상적으로 동작하는지 확인한다.
1
$ ansible all -m raw -a "hostname" -k
- provisioning 노드에서 deepops 전체 설정 정보를 수정한다.
1
$ vi ./config/group_vars/all.yml
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 222 223 224 225 226 227 228 229 230 231 232 233 234 235 236 237 238 239 240 241 242 243 244 245 246 247 248 249 250 251 252 253 254 255 256 257 258 259 260 261 262 263 264 265 266 267 268 269 270 271 272 273 274 275 276 277 278 279 280 281 282 283 284 285 286 287 288 289 290 291 292 293 294 295 296 297 298 299 300 301 302 303 304 305 306 307 308 309 310
################################################################################ # DeepOps Ansible Config # ################################################################################ # # Configuration common to all hosts # Define per-group or per-host values in the other configuration files # ################################################################################ # PROXY ################################################################################ # Proxy Variables needed for scripts, ansible, etc. # http_proxy: http://10.0.2.5:3128 # https_proxy: http://10.0.2.5:3128 # no_proxy: localhost,cluster.local,127.0.0.1,::1,10.0.2.10,10.0.2.20,10.0.2.30 # proxy_env: # http_proxy: '{{ http_proxy }}' # https_proxy: '{{ https_proxy }}' # no_proxy: '{{ no_proxy }}' ################################################################################ # NETWORK # ################################################################################ # DNS config # Playbook: dns-config #dns_config_servers: [8.8.8.8] #dns_config_search: [example.com] # NTP configuration # Playbook: chrony-client chrony_install: true chrony_service_state: "started" chrony_service_enabled: "yes" chrony_timezone: "Etc/UTC" chrony_config_server: - 0.pool.ntp.org - 1.pool.ntp.org - 2.pool.ntp.org - 3.pool.ntp.org # Set hostname based on inventory file # ☆ 다음을 변경 : 서버의 호스트명을 임의로 변경하지 않고, ansible에서의 호스트명을 서버의 호스트명으로 수동으로 맞추도록 함 (inventory 파일에서 수행) deepops_set_hostname: false ################################################################################ # SOFTWARE # ################################################################################ # Extra software to install or remove # Playbook: software #software_extra_packages: # - curl # - git # - rsync # - screen # - tmux # - vim # - wget # - build-essential # - linux-tools-generic # - "{{ 'linux-headers-' + ansible_kernel }}" #software_remove_packages: # - popularity-contest ################################################################################ # STORAGE # ################################################################################ # AutoFS configuration # Playbook: authentication #autofs_mount: "/home" #autofs_map: "auto.home_linux" # NFS Server # This config will create an NFS server and share the given exports # Playbook: nfs-server.yml #nfs_exports: # - path: /export/shared # options: "*(rw,sync,no_root_squash)" # NFS Client # This config will mount an NFS share on hosts # Playbook: nfs-client.yml #nfs_mounts: # - mountpoint: /mnt/shared # server: '{{ groups["slurm-master"][0] }}' # path: /export/shared # options: async,vers=3 # Extra Packages for Enterprise Linux (RHEL/CentOS) epel_package: "https://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/epel-release-latest-{{ ansible_distribution_major_version }}.noarch.rpm" ################################################################################ # USERS # ################################################################################ # User management # Playbook: users, user-password # create user `nvidia` with password `deepops` on all nodes users: - username: nvidia name: nvidia password: $6$IrxI27V4ogJFfgTV$RvNskQFvXZzE9AFsIokuXKwDAyqs9Jd03Trfi7DsHoCyllK79/zhAciZPENt4.2uRNMR0gE6.mRD/o9jP7WcZ. groups: ['sudo'] uid: 10007 home: /home/nvidia ################################################################################ # SSH HARDENING # # dev-sec.ssh-hardening role called from users playbook # ################################################################################ ssh_client_hardening: false ssh_server_password_login: true ssh_use_pam: true ssh_max_auth_retries: 10 sftp_enabled: true sftp_chroot: false ################################################################################ # NVIDIA # ################################################################################ # NVIDIA GPU configuration # Playbook: nvidia-cuda cuda_version: cuda-toolkit-11-5 # DGX-specific vars may be used to target specific models, # because available versions for DGX may differ from the generic repo #cuda_dgx_1_version: "{{ cuda_version }}" #cuda_dgx_2_version: "{{ cuda_version }}" #cuda_dgx_a100_version: "{{ cuda_version }}" # Playbook: nvidia-set-gpu-clocks # Resets the Gpu clocks to the default values. (see the `--reset-gpu-clocks` flag in nvidia-smi for more) gpu_clock_reset: no # Specifies <minGpuClock,maxGpuClock> clocks as a pair (e.g. 1500,1500) that defines the range of desired locked GPU clock speed in MHz. Setting this will supersede application clocks and take effect regardless if an app is running. Input can also be a singular desired clock value. (see the `--lock-gpu-clocks` flag in nvidia-smi for more) gpu_clock_lock: "1507,1507" # Debugging var: force install NVIDIA driver even if GPU not detected nvidia_driver_force_install: false ################################################################################ # CONTAINER RUNTIME # ################################################################################ # Docker configuration # Playbook: docker, nvidia-docker, k8s-cluster # # For supported Docker versions, see: kubespray/roles/container-engine/docker/vars/* docker_install: yes docker_version: '20.10' docker_dns_servers_strict: no docker_storage_options: -s overlay2 #docker_options: "--bip=192.168.99.1/24" # Enable docker iptables # If this isn't set, containers won't have access to the outside net # See https://github.com/kubernetes-sigs/kubespray/issues/2002 docker_iptables_enabled: true # Docker daemon logins # Note: example only! you should put these in an Ansible Vault file for security! # #docker_login_registries: #- registry: docker.io # username: myuser # password: mypassword # email: docker@docker.io #- registry: nvcr.io # username: '$oauthtoken' # password: mypassword # Enroot configuration # Playbook: slurm, slurm-cluster # # See: https://github.com/NVIDIA/pyxis/wiki/Setup#enroot-configuration-example enroot_runtime_path: '/run/enroot/user-$(id -u)' enroot_cache_path: '/var/lib/enroot-cache/user-$(id -u)' enroot_data_path: '/tmp/enroot-data/user-$(id -u)' enroot_config: | ENROOT_CONFIG_PATH ${HOME}/.config/enroot ENROOT_SQUASH_OPTIONS -noI -noD -noF -noX -no-duplicates ENROOT_MOUNT_HOME y ENROOT_RESTRICT_DEV y ENROOT_ROOTFS_WRITABLE y ENROOT_RUNTIME_PATH {{ enroot_runtime_path }} ENROOT_CACHE_PATH {{ enroot_cache_path }} ENROOT_DATA_PATH {{ enroot_data_path }} enroot_environ_config_files: [] enroot_environ_config_files_dgx: - filename: 50-mellanox.env content: | MELLANOX_VISIBLE_DEVICES=all - filename: 50-mpi.env content: | OMPI_MCA_btl_tcp_if_exclude=lo,docker0,ib0,ib1,ib2,ib3 # Singularity configuration # Playbook: singularity, slurm-cluster # Singularity target version singularity_version: "3.7.3" singularity_conf_path: "/etc/singularity/singularity.conf" bind_paths: [] # example: #- /mnt/shared golang_install_dir: '/opt/go/{{ golang_version }}' golang_gopath: /opt/go/packages ################################################################################ # AUTH # ################################################################################ # NIS configuration # Playbook: authentication #nis_domain: example.com #nis_server: 10.0.0.1 # Kerberos configuration # Playbook: authentication #kerberos_client_realm_name: "example.com" #kerberos_client_kdc_hostname: "kerberos" #kerberos_client_admin_hostname: "kerberos" #nfs_idmapd_domain: example.com ################################################################################ # MONITORING # ################################################################################ # Collectd # Playbook: collectd #collectd_network_server: "deepops-mgmt.example.com" #collectd_network_port: "30300" #collectd_python_module_path: "/usr/lib/collectd/dcgm" #collectd_python_modules: [] #collectd_config_dir: "/etc/collectd/collectd.conf.d" #with_dcgm_collectd: false ################################################################################ # MAAS # ################################################################################ # MAAS (Metal as a Service): Node provisioning/PXE service # Playbook: maas, maas_management maas_adminusers: - username: 'admin' email: 'admin@{{ maas_dns_domain }}' password: 'admin' maas_dns_domain: 'deepops.local' maas_region_controller: '192.168.1.1' maas_region_controller_url: 'http://{{ maas_region_controller }}:5240/MAAS' maas_repo: 'ppa:maas/2.8' # Defines if maas user should generate ssh keys # Usable for remote KVM/libvirt power actions maas_setup_user: false maas_single_node_install: true maas_kvm: false ################################################################################ # NVIDIA Datacenter GPU Manager # ################################################################################ install_dcgm: true ################################################################################ # Misc. # ################################################################################ # Set /etc/rc.local contents # Playbook: rc-local # rc_local_contents: | # echo foo # echo bar # # DeepOps specific config deepops_dir: /opt/deepops # Directory for python virtualenv # Roles: K8s GPU operator, GPU plugin, OpenShift/K8s deepops_venv: '{{ deepops_dir }}/venv' # OpenMPI # Playbook: openmpi openmpi_version: 4.0.3 # Disable cloud-init # ☆ 다음을 변경 deepops_disable_cloud_init: false # Default profile when using NVIDIA MIG Manager: https://github.com/NVIDIA/mig-parted mig_manager_profile: all-disabled mig_manager_config: /etc/nvidia-mig-manager/config.yml mig_manager_hooks: /etc/nvidia-mig-manager/hooks.yaml ################################################################################ # Container registry # ################################################################################ # ☆ 다음을 변경 standalone_container_registry_cache_enable: false standalone_container_registry_port: "5000" # To configure some set of hosts as insecure registries, list them here. # Slurm and K8s cluster playbooks will automatically use the master nodes for # these if not specified. #docker_insecure_registries: ["<host>:<port>"] #docker_registry_mirrors: ["http://<host>:<port>"] ################################################################################ # Configuration for NGC-Ready playbook # ################################################################################ ngc_ready_cuda_container: "nvcr.io/nvidia/cuda:10.1-base-ubuntu18.04" ngc_ready_pytorch: "nvcr.io/nvidia/pytorch:18.10-py3" ngc_ready_tensorflow: "nvcr.io/nvidia/tensorflow:18.10-py3"
- provisioning 노드에서 deepops slurm-cluster 설정 정보를 수정한다.
1
$ vi ./config/group_vars/slurm-cluster.yml
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 222 223 224 225 226 227 228 229 230 231 232
################################################################################ # Slurm # ################################################################################ # Slurm job scheduler configuration # Playbook: slurm, slurm-cluster, slurm-perf, slurm-perf-cluster, slurm-validation slurm_version: "21.08.8-2" slurm_install_prefix: /usr/local pmix_install_prefix: /opt/deepops/pmix hwloc_install_prefix: /opt/deepops/hwloc #slurm_user_home: /local/slurm slurm_manage_gpus: true #slurm_cluster_name: deepops #slurm_username: slurm slurm_password: ReplaceWithASecurePasswordInTheVault #slurm_db_username: slurm slurm_db_password: AlsoReplaceWithASecurePasswordInTheVault #slurm_max_job_timelimit: INFINITE #slurm_default_job_timelimit: # Ensure hosts file generation only runs across slurm cluster hosts_add_ansible_managed_hosts_groups: ["slurm-cluster"] # Enable Slurm high-availability mode # NOTE: The location for Slurm saved state needs to reside in a location shared by all Slurm controller nodes # Ideally this is on external NFS server and not the primary control node, since its failure # would also take down that NFS share slurm_enable_ha: false slurm_ha_state_save_location: "/sw/slurm" # Slurm configuration is auto-generated from templates in the `slurm` role. # If you want to override any of these files with custom config files, please # set the following vars to the absolute path of your custom files. # #slurm_conf_template: "/path/to/slurm.conf" #slurm_cgroup_conf_template: "/path/to/cgroup.conf" #slurm_gres_conf_template: "/path/to/gres.conf" #slurm_dbd_conf_template: "/path/to/slurmdbd.conf" ################################################################################ # Login on compute ################################################################################ # Restrict user SSH access to only allow users with a running job slurm_restrict_node_access: true # List users who should always be able to SSH, even without a running job slurm_allow_ssh_user: [] # Enable a Slurm compute node to also function as a login node. # This is needed for the "single node Slurm cluster" configuration. # See docs/slurm-cluster/slurm-single-node.md slurm_login_on_compute: false ################################################################################ # Optional installs # ################################################################################ slurm_configure_etc_hosts: yes dns_mode: none # ☆ 다음을 변경 slurm_cluster_install_cuda: no # ☆ 다음을 변경 slurm_cluster_install_nvidia_driver: no slurm_cluster_install_singularity: no ################################################################################ # NFS # ################################################################################ # Default exports: # - /home: shared home directories, needed for Open OnDemand and best practice # - /sw: shared space for software installs, used for Spack or EasyBuild nfs_exports: - path: /home options: "*(rw,sync,no_root_squash)" - path: /sw options: "*(rw,sync,no_root_squash)" nfs_mounts: - mountpoint: /home server: '{{ groups["slurm-master"][0] }}' path: /home options: async,vers=3 - mountpoint: /sw server: '{{ groups["slurm-master"][0] }}' path: /sw options: async,vers=3 # Flags for enable/disable of NFS deployment # - Set up an NFS server on nfs-server? # ☆ 다음을 변경 slurm_enable_nfs_server: false # - Mount NFS filesystems on nfs-clients? # ☆ 다음을 변경 slurm_enable_nfs_client_nodes: false # Inventory host groups to use for NFS server or clients nfs_server_group: "slurm-master[0]" nfs_client_group: "slurm-master[1:],slurm-node" ################################################################################ # SOFTWARE MODULES (SM) # # May be built with either EasyBuild or Spack # ################################################################################ # ☆ 다음을 변경 slurm_install_lmod: false # Note: the sm_prefix must be in an NFS-shared location sm_prefix: "/sw" # Easybuild-specific sm_module_root: "{{ sm_prefix }}/modules" sm_software_path: "{{ sm_prefix }}/software" sm_files_path: "{{ sm_prefix }}/easybuild_files" sm_sources_path: "{{ sm_prefix }}/sources" sm_build_path: "{{ sm_prefix }}/build" sm_files_url: "https://github.com/DeepOps/easybuild_files.git" sm_install_default: true sm_module_path: "{{ sm_module_root }}/all" # Spack-specific spack_install_dir: "{{ sm_prefix }}/spack" spack_build_packages: false spack_default_packages: - "cuda@10.2.89" - "openmpi@3.1.6 +cuda +pmi schedulers=auto" # Which host should we run installs on for software going into the NFS share? sm_install_host: "slurm-master[0]" ################################################################################ # NVIDIA HPC SDK # ################################################################################ # ☆ 다음을 변경 slurm_install_hpcsdk: false # Select the version of HPC SDK to download hpcsdk_major_version: "22" hpcsdk_minor_version: "1" hpcsdk_file_cuda: "11.5" hpcsdk_arch: "x86_64" # In a Slurm cluster, default to setting up HPC SDK as modules rather than in # the default user environment # ☆ 다음을 변경 hpcsdk_install_as_modules: false hpcsdk_install_in_path: false ################################################################################ # OpenMPI build # # # # The openmpi.yml playbook will build a custom-configured OpenMPI based on the # # Slurm, PMIx, and hwloc on the cluster. In most cases you should be fine with # # using the OpenMPI provided in the HPC SDK, but if you need a custom build, # # this can help you get started. ################################################################################ slurm_cluster_install_openmpi: false openmpi_version: 4.0.4 openmpi_install_prefix: "/usr/local" openmpi_configure: "./configure --prefix={{ openmpi_install_prefix }} --disable-dependency-tracking --disable-getpwuid --with-pmix={{ pmix_install_prefix }} --with-hwloc={{ hwloc_install_prefix }} --with-pmi={{ slurm_install_prefix }} --with-slurm={{ slurm_install_prefix }} --with-libevent=/usr" ################################################################################ # Open OnDemand # ################################################################################ install_open_ondemand: no # OOD Linux-host adapter requires `slurm_cluster_install_singularity` to be true ood_install_linuxhost_adapter: no servername: '{{ ansible_fqdn }}' httpd_port: 9050 httpd_listen_addr_port: - 9050 httpd_use_rewrites: false node_uri: /node rnode_uri: /rnode ################################################################################ # Allow the User Permission to Set GPU Clocks # ################################################################################ allow_user_set_gpu_clocks: no ################################################################################ # Enroot & Pyxis # ################################################################################ # ☆ 다음을 변경 slurm_install_enroot: false # ☆ 다음을 변경 slurm_install_pyxis: false slurm_pyxis_version: 0.11.1 ################################################################################ # Node Health Check # ################################################################################ # ☆ 다음을 변경 slurm_install_nhc: no slurm_health_check_program: "/usr/sbin/nhc" # The health check configuration generated by default in DeepOps is pretty # basic, and most cluster administrators will want to set up more extensive # NHC configurations with their local site customizations. # To set a custom file for Ansible to provision to /etc/nhc/nhc.conf, set the # following var: # #nhc_config_template: "/path/to/custom/nhc.conf" # # For documentation on the file format, see: # https://github.com/mej/nhc/blob/master/README.md ################################################################################ # Container registry # ################################################################################ # ☆ 다음을 변경 slurm_enable_container_registry: false docker_insecure_registries: "{{ groups['slurm-master'] | map('regex_replace', '^(.*)$', '\\1:5000') | list + ['registry.local:31500'] }}" docker_registry_mirrors: "{{ groups['slurm-master'] | map('regex_replace', '^(.*)$', 'http://\\1:5000') | list }}" ################################################################################ # Monitoring stack # ################################################################################ slurm_enable_monitoring: true # Inventory host groups where cluster monitoring services will be installed # (Prometheus, Grafana, etc) slurm_monitoring_group: "slurm-master" ################################################################################ # Logging with rsyslog # ################################################################################ # ☆ 다음을 변경 slurm_enable_rsyslog_server: false # ☆ 다음을 변경 slurm_enable_rsyslog_client: false rsyslog_server_hostname: "{{ groups['slurm-master'][0] }}" rsyslog_client_tcp_host: "{{ rsyslog_server_hostname }}" rsyslog_client_group: "slurm-cluster"
- provisioning 노드에서 deepops slurm-cluster 설치 정보를 수정한다.
1
$ vi ./playbooks/slurm-cluster.yml
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146
# ☆ 다음을 변경 (모두 주석 처리 후, 3개 부분만 주석 해제) --- # Slurm Cluster Playbook # Install python required for Ansible #- include: bootstrap/bootstrap-python.yml # Set up passwordless sudo and SSH keys if needed #- include: bootstrap/bootstrap-ssh.yml #- include: bootstrap/bootstrap-sudo.yml # Disable cloud-init #- include: generic/disable-cloud-init.yml # when: deepops_disable_cloud_init # Configure hostnames, /etc/hosts # ☆ 다음을 주석 처리 해제 - include: generic/hosts.yml when: "{{ slurm_configure_etc_hosts | default(true) }}" tags: - set-etc-hosts # Configure Chrony (NTP) sync #- include: generic/chrony-client.yml # when: chrony_install|default(true) # Set up a local cluster container registry #- include: container/standalone-container-registry.yml hostlist=slurm-master # when: slurm_enable_container_registry|default(true) # Set up NGINX-based container caching #- include: container/nginx-docker-registry-cache-server.yml # vars: # hostlist: "{{ nginx_docker_cache_hostgroup | default('slurm-cache') }}" # when: slurm_enable_nginx_docker_cache | default(false) #- include: container/nginx-docker-registry-cache-client.yml # vars: # hostlist: "{{ nginx_docker_cache_clients | default('slurm-node') }}" # when: slurm_enable_nginx_docker_cache | default(false) # Install NVIDIA driver #- include: nvidia-software/nvidia-driver.yml # when: slurm_cluster_install_nvidia_driver|default(true) # Install NVIDIA CUDA Toolkit # Note: the CUDA playbook also installs the driver, so we pass the # appropriate flag to this playbook as well. #- include: nvidia-software/nvidia-cuda.yml # vars: # cuda_playbook_install_driver: "{{ slurm_cluster_install_nvidia_driver }}" # when: slurm_cluster_install_cuda|default(true) # Install software #- include: generic/software.yml # Set up NFS filesystem #- include: generic/nfs-server.yml # vars: # hostlist: "{{ nfs_server_group | default('slurm-nfs[0]') }}" # when: slurm_enable_nfs_server #- include: generic/nfs-client.yml # vars: # hostlist: "{{ nfs_client_group | default('slurm-nfs-client') }}" # when: slurm_enable_nfs_client_nodes # Install DCGM #- include: nvidia-software/nvidia-dcgm.yml hostlist=slurm-node # when: install_dcgm|default(false) # Install Node Health Check #- include: slurm-cluster/nhc.yml hostlist=slurm-node # when: slurm_install_nhc|default(false) # Install Slurm #- include: slurm-cluster/slurm.yml # Install OpenMPI #- include: slurm-cluster/openmpi.yml # when: slurm_cluster_install_openmpi|default(true) # Install Lmod #- include: slurm-cluster/lmod.yml # when: slurm_install_lmod # Install the NVIDIA HPC SDK #- include: nvidia-software/nvidia-hpc-sdk.yml # vars: # hostlist: "{{ sm_install_host | default('slurm-login[0]')}}" # when: slurm_install_hpcsdk # Install monitoring services # ☆ 다음을 주석 처리 해제 - include: slurm-cluster/prometheus.yml vars: hostlist: "{{ slurm_monitoring_group | default('slurm-metric') }}" when: slurm_enable_monitoring - include: slurm-cluster/grafana.yml vars: hostlist: "{{ slurm_monitoring_group | default('slurm-metric') }}" when: slurm_enable_monitoring # Install monitoring exporters #- include: slurm-cluster/prometheus-slurm-exporter.yml # vars: # hostlist: "{{ slurm_monitoring_group | default('slurm-metric') }}" # when: slurm_enable_monitoring # ☆ 다음을 주석 처리 해제 - include: slurm-cluster/prometheus-node-exporter.yml when: slurm_enable_monitoring - include: slurm-cluster/nvidia-dcgm-exporter.yml when: slurm_enable_monitoring # Set up rsyslog forwarding from compute nodes to head node #- include: generic/rsyslog-server.yml # vars: # hostlist: "{{ rsyslog_server_hostname | default('slurm-master[0]') }}" # when: slurm_enable_rsyslog_server|default(true) #- include: generic/rsyslog-client.yml # vars: # hostlist: "{{ rsyslog_client_group | default('slurm-node') }}" # when: slurm_enable_rsyslog_client|default(true) # Install Singularity #- include: container/singularity.yml # when: slurm_cluster_install_singularity|default(true) # Install Open OnDemand #- include: slurm-cluster/open-ondemand.yml # when: install_open_ondemand # Set Permissions to adjust GPU Clocks speeds #- include: utilities/gpu-clocks.yml # when: allow_user_set_gpu_clocks # Install Enroot and Pyxis #- include: container/pyxis.yml # when: # - slurm_install_enroot # - slurm_install_pyxis # tags: # - pyxis # Ensure that nv_peer_mem is loaded #- include: nvidia-software/nvidia-peer-memory.yml # tags: # - nvidia-peer-memory
- (Optional: nvidia driver, docker 설치는 되어 있다고 가정하는 경우 ★) provisioning 노드에서 deepops nvidia-dcgm-exporter 설치 정보를 수정한다.
1
$ vi ./playbooks/slurm-cluster/nvidia-dcgm-exporter.yml
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20
--- # ☆ 다음을 주석 처리 #- include: ../container/docker.yml #- include: ../nvidia-software/nvidia-driver.yml #- include: ../container/nvidia-docker.yml - hosts: "{{ hostlist | default('all') }}" become: yes tasks: - name: install custom facts module include_role: name: facts - name: set GPU fact set_fact: has_gpus: true when: ansible_local['gpus']['count'] - name: configure dcgm exporter include_role: name: nvidia-dcgm-exporter when: ansible_distribution == "Ubuntu" or ansible_os_family == "RedHat"
- Slurm Cluster를 설치한다.
1 2 3 4
# NOTE: If SSH requires a password, add: `-k` # NOTE: If sudo on remote machine requires a password, add: `-K` # NOTE: If SSH user is different than current user, add: `-u ubuntu` $ ansible-playbook -kK -l slurm-cluster playbooks/slurm-cluster.yml
접속
- master 노드의 node-exporter - 192.168.30.119:9100/metrics
- master 노드의 dcgm-exporter - 192.168.30.119:9400/metrics
- worker 노드의 node-exporter - 192.168.30.121:9100/metrics
- worker 노드의 dcgm-exporter - 192.168.30.121:9400/metrics
- master 노드의 prometheus - 192.168.30.119:9090/graph
- master 노드의 grafana - 192.168.30.119:3000
참고
- Slurm Deployment Guide https://github.com/NVIDIA/deepops/tree/master/docs/slurm-cluster
 Copyrightⓒ2022 Develiberta All rights reserved.
Copyrightⓒ2022 Develiberta All rights reserved.